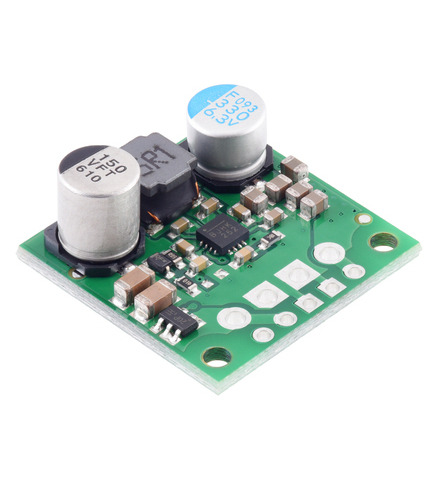
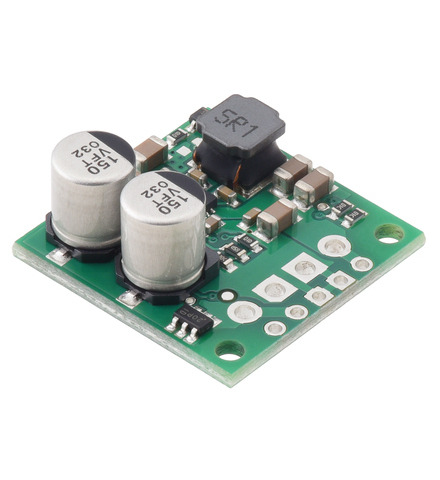
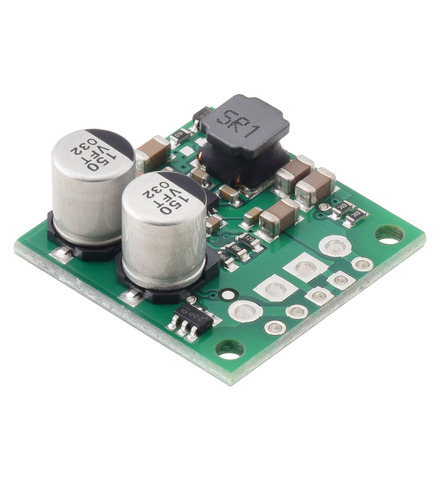
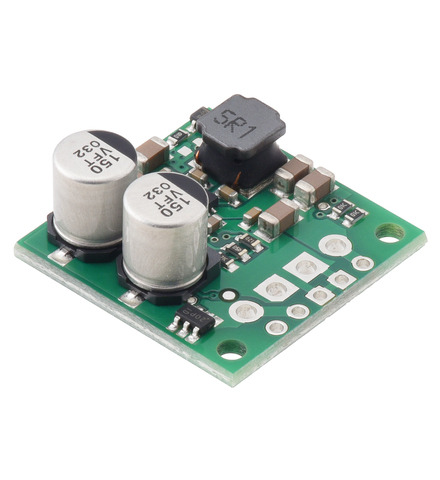
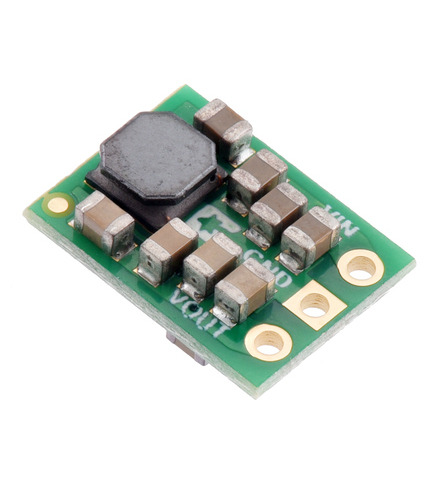
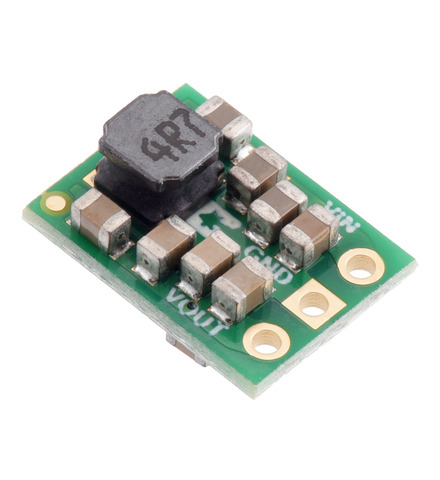
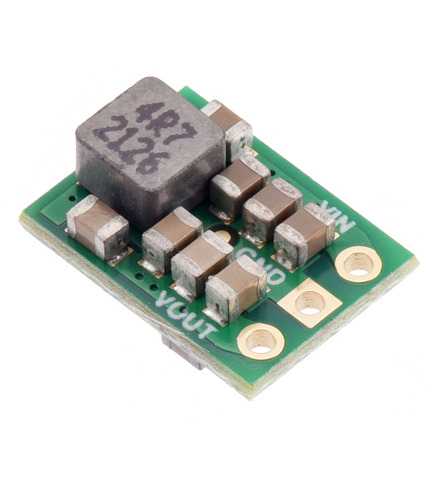
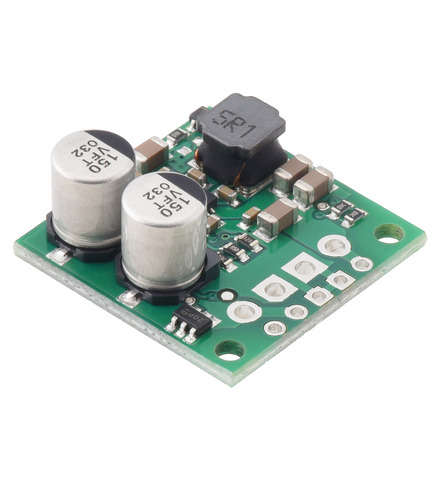
The S13VxFx family of efficient switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters) use a buck-boost topology to take an input voltage from 2.8 V to 22 V and increase it or decrease it as necessary to produce the desired regulated output voltage. They offer typical efficiencies of over 85% and typical maximum continuous output currents between 1 A and 3 A . The flexibility in input voltage offered by this family of regulators is especially well-suited for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below the regulated voltage. Without the typical restriction on the battery voltage staying above the required voltage throughout its life, new battery packs and form factors can be considered.
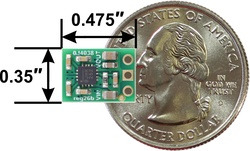 | 5V, 1A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V10F5, bottom view with dimensions. |
|---|
|
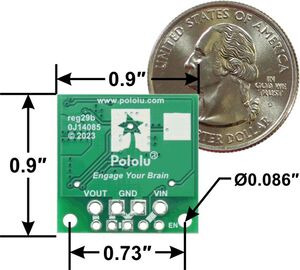 | Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V25Fx, bottom view with dimensions. |
|---|
|
This family includes several extra-compact (0.35″ × 0.475″) versions that output a fixed 5 V with different maximum output current capabilities along with a set of larger (0.9″ × 0.9″) versions that can do even more current with output voltages from 3.3 V through 15 V. These larger units have reverse-voltage protection up to 20 V while the smaller units do not have reverse-voltage protection.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category
Products in category “S13VxFx Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulators”
This tiny synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 5 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 5 V. The extra-compact board measures 0.35″ × 0.475″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply a typical continuous output current of around 1 A.
This tiny synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 5 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 5 V. The extra-compact board measures 0.35″ × 0.475″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 1 A and 2 A depending on the input voltage.
This tiny synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 5 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 5 V. The extra-compact board measures 0.35″ × 0.475″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 1 A and 2.5 A depending on the input voltage.
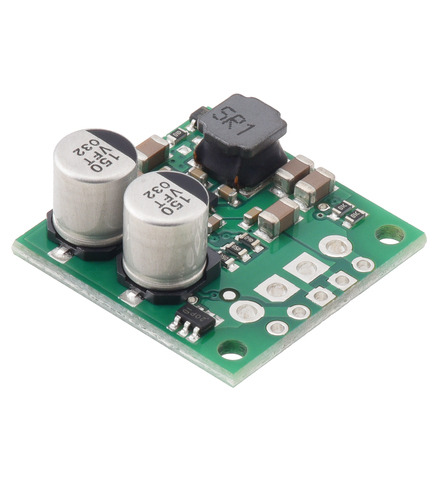
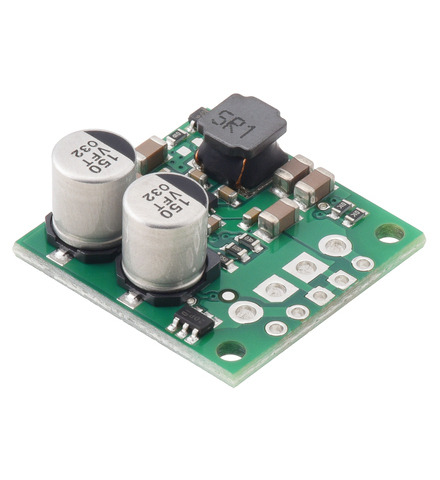
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 5 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 5 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 2 A and 4 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 3.3 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 3.3 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 2.5 A and 3.5 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 6 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 6 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 1.5 A and 3.5 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 7.5 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 7.5 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 1 A and 3.5 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 9 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 9 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 1 A and 3 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 12 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 12 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 0.5 A and 3 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
This synchronous switching step-up/step-down regulator efficiently produces 15 V from input voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V. Its ability to convert both higher and lower input voltages makes it useful for applications where the power supply voltage can vary greatly, as with batteries that start above but discharge below 15 V. The board measures 0.9″ × 0.9″, has a typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, and can supply typical continuous output currents between 0.5 A and 3 A depending on the input voltage. The regulator also features reverse voltage protection and an optional enable input that can be used to put the regulator in a low-power state with a current draw of less than 10 µA per volt on VIN.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category